
Industrial Participation in STC Activities
Industry is involved in STC activities in several ways that influence the direction of research. Industry participation revolves around several knowledge transfer activities, including participation in center management and advisory committees, visitors programs, industrial affiliates programs, and use of STC resources. This participation has resulted in the creation of new tools, methodology, software, and spinoff companies.- Advisory Committees and Center Management
- The importance of the STC program to industry can
be effectively highlighted by the direct role that industry plays in center management and direction. More
than 20 STCs have an external advisory committee with members from industry. These members
contribute to the centers direction in research and provide feedback on the types of knowledge transfer
activities.
At the Center for Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science, a consortium of Princeton University, Rutgers University, AT&T Bell Laboratories and Bellcore, more than 55 scientists from these companies are members. The Center for Photoinduced Charge Transfer has a similar partnership with pre-competitive research, facilities, and ownership in technologies shared between the University of Rochester, Xerox, and Eastman Kodak. Every funded project has at least one industry leader on the project team.
- Industrial Affiliates and Visitors
- The affiliates programs promote research collaboration, industrial
access to technical reports, and overall guidance of center research. Most affiliate programs are tailored to
the center. For example, the Center for Engineering Plants for Resistance Against Pathogens (CEPRAP)
has a strong incentive program that gives affiliates equal access to all CEPRAP inventions, with increased
access for greater support.
Knowledge transfer through affiliates programs create and solidify the bonds between centers and their affiliates.
To enhance long-term collaboration between center and industry researchers, the STCs also sponsor visitors programs, such as the Center for Quantized Electronic Structures' "Scholar-in-Residence" program. Through the "Industrial Fellows" program at the Center for Biological Timing, researchers at the Promega Corporation have collaborated with the center, using imaging facilities to develop new ways to non-invasively measure the activity of genes in living tissues.
- Shared Resources
- Whether it is facilities or information, industry can draw upon the
tremendous resources that the STCs have to offer. The resource facility at the Center for Advanced Liquid
Crystalline Optical Materials provides synthesis, characterization, and prototyping services to companies,
national laboratories and universities. The Center for High Performance Polymeric Adhesives and
Composites operates an Intron High-temperature Axial-Torsional Testing Machine, the only machine of
its kind in the world that is specifically designed to test ceramic composites at temperatures of up to 1500
degrees centigrade.
Some centers maintain extensive databases on specialized subjects that can be used as resources for industry. For example, the Southern California Earthquake Center has established a database of earthquake information for use by engineers and emergency preparedness personnel. The Center for Ultrafast Optical Science and the Center for Superconductivity are currently developing a database for commercial superconductor device design and modeling data collected from industry samples. Through the Linguistic Data Consortium, the Center for Research in Cognitive Science has created text and speech databases as a national resource for human language technology. Many small businesses have used these databases, making it economically feasible to expand their research into areas where prohibitive costs formerly existed.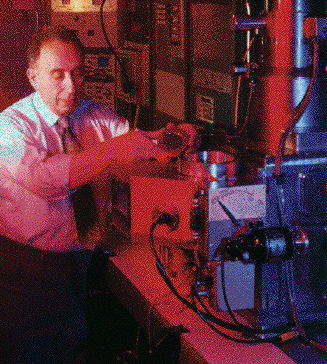
This vector scan electron beam litography machine is central to cutting-edge research on ultra-small semiconductor structures - Center for Quantized Electronic Structures - Small Business Collaboration and Development
- Small businesses that offer specialized products and
services use the STC program as an information and technology resource. For instance, the Center for
Advanced Cement-Based Materials worked with the State of Illinois to develop knowledge transfer
partnerships with small businesses in Illinois. As a result, more than 60 leaders in the cement and
construction industry have met with ACBM faculty and staff to identify barriers related to knowledge
transfer and to discuss strategies to enhance the role of innovation in this industry.
Centers have also worked on a one-on-one basis with small businesses. Ability Engineering Technology, a small engineering and design firm, has worked with the Center for Magnetic Resonance Technology for Basic Biological Research to refine its engineering and manufacturing skills, and utilize new technologies to reduce costs. As another example, the Center for Quantized Electronic Structures has provided Sputtered Films Inc. considerable expertise on novel dry etching processes.
Technologies developed from STC research have also led to small businesses created to market these technologies. For example:
- At The Geometry Center, a scientist has started Minerva Software Inc. to commercialize a programming system for computer animation.
- Three companies have been started by researchers at the Center for Ultrafast Optical Science. Picotronix produces ultrafast optoelectronics parts for use in other manufacturer's systems, Medox Research produces ultrahigh peak power lasers, and Terametrics produces high-speed optoelectronic sensors that characterize electronic materials.
- The Illinois Superconductor Corporation, a company that develops materials for magnets and wires, was spun off from a research group at the Center for Superconductivity. The center has worked closely with the company, winning grants for commercial product development and other projects.
- Researchers from the Center for Molecular Biotechnology have created a new company called Darwin Molecular Technologies to offer commercial services in DNA sequencing and applied molecular evolution.
Knowledge Transfer Activities
Sites & Affiliations | Leadership | Research & Applications | Major Accomplishments | FAQ | Search | Knowledge & Technology Transfer | Calendar of Events | Education & Outreach | Media Resources | Technical Reports & Publications | Parallel Computing Research Quarterly Newsletter | News Archives | Contact Information
| Hipersoft | CRPC |
© 2003 Rice University
|